Engagement in strength training activities is associated with a plethora of advantages, including augmented fat oxidation, prevention of musculoskeletal injuries, elevation of mood, and enhancement of general health. Alas, a mere fraction, less than 30%, of American adults adhere to the minimum standards for muscle-strengthening activities. Mastery of proper exercise technique is paramount for achieving optimal outcomes and averting potential injuries. This comprehensive guide elucidates the essential aspects of proper form in strength training exercises, encompassing safety protocols, appropriate equipment selection, and methodologies for targeting diverse muscle groups.
When executed with precision in lifting mechanics and muscle activation, strength training can profoundly elevate one’s fitness and health levels. Adherence to the principles outlined in this guide will empower you to execute strength training exercises with exemplary form, thus maximizing benefits while minimizing injury risk.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Strength Training Safety
When engaging in strength training, safety must be paramount. Initiate with 5-10 minutes of light cardio or gentle sets to prepare your muscles and joints. It is imperative to maintain good posture throughout your exercises, ensuring slow movements to isolate the target muscles and proper breathing to prevent breath-holding.
Excessive haste or overexertion during your workout significantly elevates the risk of injury prevention. Always heed your body’s signals and cease immediately if you encounter any pain or discomfort. The selection of appropriate, stable footwear is critical for workout safety and support during lifts.
Rest and recovery are equally vital to the workout itself. Ensure at least one day of rest between sessions targeting the same muscle groups to facilitate your body’s repair and rebuilding processes. Adequate sleep and proper nutrition are indispensable in supporting your strength training objectives and minimizing injury risks.
Incorporating warmup routines before your strength training session, adhering to proper form, and prioritizing rest and recovery are fundamental to cultivating a sustainable and safe fitness regimen. Adherence to these foundational principles enables you to maximize the benefits of strength training while minimizing the risk of setbacks due to injuries.
Essential Equipment and Preparation for Strength Training
Choosing the Right Equipment
Initiation into strength training often commences with bodyweight exercises. Progression necessitates the acquisition of basic apparatus such as resistance bands, dumbbells, and an exercise ball. These tools serve to intensify muscle engagement and facilitate the attainment of fitness objectives. Opt for weights that accommodate a variety of exercises and target multiple muscle groups. Adjustable dumbbells, in particular, offer a dual advantage of versatility and the ability to incrementally increase resistance as one’s strength evolves.
Pre-workout Preparation
Antecedent to any strength training regimen, meticulous preparation is paramount. Initiate by configuring your workout environment, ensuring that all apparatus is in pristine condition and operational. The availability of water is imperative for hydration during the exercise. For those training in a gym setting, leverage any offered orientations or guidance to master the correct utilization of equipment and techniques.
| Exercise Equipment | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Free Weights (Dumbbells, Barbells, Kettlebells) | Offer a wider range of motion and allow for specific muscle targeting |
| Weight Machines | Provide muscle isolation, safety features for beginners, time efficiency, and easier progressive overload |
| Resistance Bands | Feature convenience, affordability, low impact on joints, improved balance, coordination, and flexibility |
| Bodyweight Exercises | Offer convenience, low impact on joints, budget-friendly options for strength and endurance building |
Integrating a diverse array of exercise equipment into your home gym or workout regimen is crucial for comprehensive muscle engagement. This approach ensures a well-rounded workout preparation. It is essential to commence with modest beginnings and incrementally expand your home gym as your strength and confidence escalate.
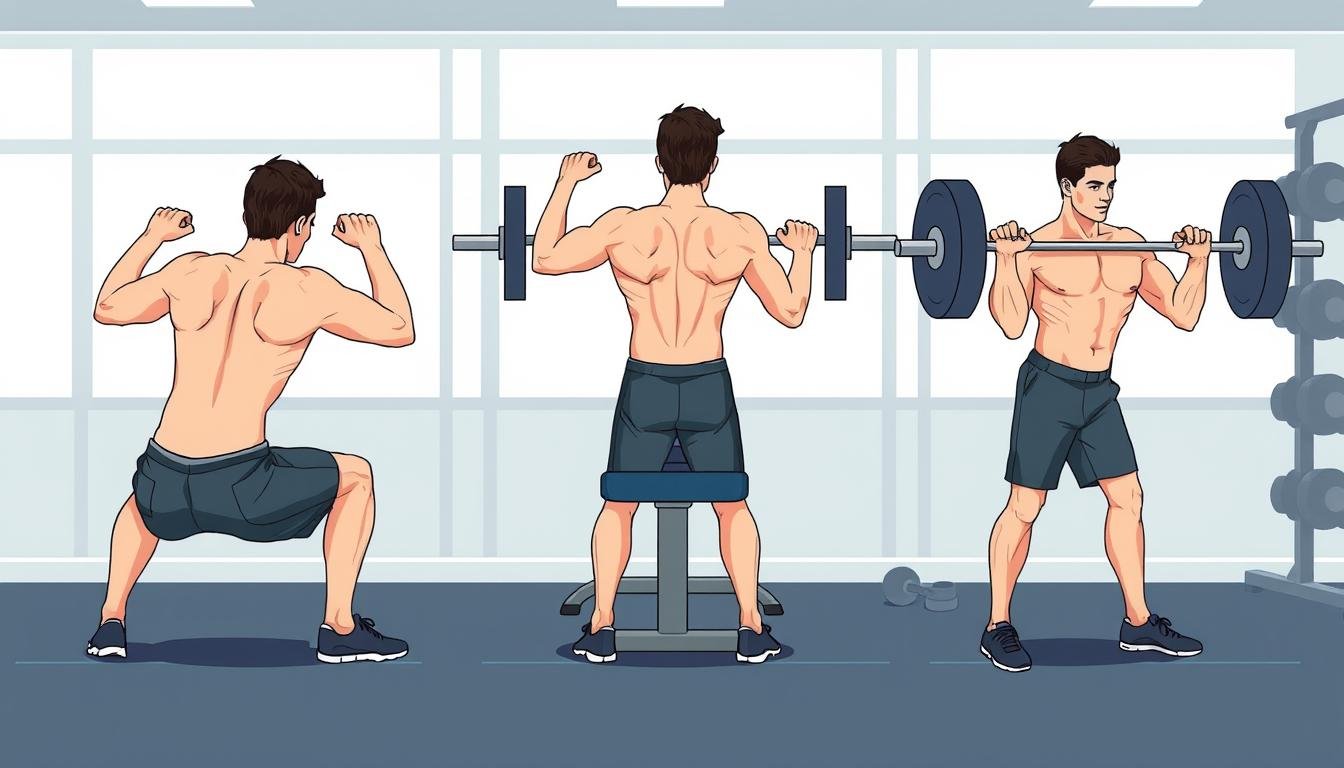
Proper Form for Strength Training Exercises
Attaining proficiency in exercise technique is paramount for the execution of safe and efficacious strength training regimens. Irrespective of one’s level of experience, adherence to correct form throughout each exercise is indispensable for precise muscle activation and the mitigation of injury risks.
Initiate your training with lighter weights, emphasizing controlled, methodical movements. It is imperative to maintain a stable core and a neutral spine alignment to bolster your body’s structural integrity during the exercise. For exercises targeting the upper body, it is crucial to keep the shoulders in a depressed and retracted position, eschewing any excessive tension in the trapezius muscles. In the realm of lower body exercises, meticulous attention to knee alignment is necessary, ensuring they remain in line with the toes.
| Muscle Group | Proper Exercise Technique |
|---|---|
| Arms | Maintain a neutral wrist position, engage the biceps, and avoid locking out the elbows. |
| Shoulders | Keep the shoulders down and back, avoid shrugging or excessive tension in the traps. |
| Chest | Squeeze the chest muscles during pressing movements, avoid arching the lower back. |
| Back | Engage the lats and maintain a neutral spine during rows and pull-ups. |
| Legs | Ensure proper knee alignment over the toes during squats and lunges. |
| Core | Brace the core to support the spine and stabilize the body during compound exercises. |
By prioritizing exercise technique, one enhances muscle activation and lifting mechanics, concurrently diminishing injury likelihood. It is advisable to commence with lighter loads, master the fundamental movement patterns, and incrementally increase the intensity as strength and confidence levels ascend.
Mastering Lower Body Exercise Techniques
The fortification of the lower extremities is paramount for comprehensive fitness and performance enhancement. Engaging in specific exercises enables the sculpting and toning of the legs, hips, and gluteal regions, concurrently fostering lean muscle development. These workouts concentrate on the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles, thus augmenting both everyday mobility and athletic prowess.
Squat Form Mechanics
The squat, a cornerstone in lower body training, engages a multitude of muscle groups through a compound movement. Initiate by standing with feet at shoulder width, core activated, and hips shifted posteriorly as knees flex. Maintain a lifted chest and ensure knee alignment over the toes. Lower down until thighs are parallel to the ground, then ascend by driving through the heels to the starting position. Achieving proficiency in the squat technique is vital for enhancing lower body strength and stability.
Deadlift Fundamentals
The deadlift, a potent exercise for the lower body, targets the glutes, hamstrings, and back muscles. Commence with feet hip-width apart, hinge at the hips, and slightly bend the knees. Maintain a neutral spine, engage the lats, and propel through the heels to lift the weight. Emphasize the hip hinge over excessive knee bend to uphold proper form. Initiate with bodyweight or light loads to refine your technique before incrementally increasing the weight.
Integrating a variety of lower body exercises, including lunges, step-ups, and Bulgarian split squats, aids in mastering the squat technique and deadlift form while diversifying lower body challenges. Prioritize correct form to optimize benefits and minimize injury risk.
Upper Body Training Form Guidelines
Attaining mastery over proper form is paramount for the execution of effective and safe upper body strength training regimens. The chest press and lat pulldown exercises stand out as pivotal components to focus on.
In the execution of the chest press, initiate by reclining on a bench with your feet firmly planted on the ground. Gradually lower the dumbbells to the vicinity of your chest, maintaining an elbow angle of 45 degrees. Activate your core muscles and exert force to elevate the weights, ensuring your shoulders remain firmly pressed against the bench. This methodical approach guarantees optimal engagement of the chest muscles while mitigating potential joint strain.
The lat pulldown exercise necessitates a high degree of form precision. Position yourself with your legs securely fastened, and adopt a grip that surpasses the width of your shoulders. Lean back marginally, engage your core, and pull the bar down to a point just beneath your chin. Emphasize the downward and backward movement of your elbows. This targeted action engages the latissimus dorsi muscles, the most expansive back muscles, leading to a more robust and defined upper body.
Adherence to controlled, deliberate movements is imperative for both the chest press and lat pulldown. Refrain from utilizing momentum or swinging the weights, as such actions can precipitate injury and undermine the efficacy of the exercises. By emphasizing the correct upper body exercise techniques, you will experience enhanced muscle engagement, augmented strength, and a diminished risk of injury or discomfort.
Recovery and Progression Strategies
Proper recovery is paramount for muscle growth and injury prevention. It necessitates at least one day of rest between strength training sessions targeting the same muscle groups. The implementation of progressive overload is crucial, incrementally increasing weight, reps, or sets to continually challenge muscles. Every 6-8 weeks, it is advisable to vary exercises and routines to prevent stagnation.
Nutrition and hydration play pivotal roles in post-workout recovery. The inclusion of stretching and foam rolling can significantly aid in muscle recovery and enhance flexibility. Continuous monitoring of progress and program adjustments are essential to meet fitness objectives.
Ensuring proper form and technique is vital to minimize the risk of muscle strain and re-injury. Balance training, which strengthens muscles and improves body position awareness, is notably beneficial for fall prevention in older adults. A holistic approach, combining resistance training, conditioning exercises, and compound movements, is indispensable for comprehensive recovery and muscle rebuilding.